English prepositions are small words that show the relationship between parts of a sentence, especially time, place, movement, cause, and connection, and they change meaning more than any other grammatical group. While most textbooks focus on memorizing a master list, English prepositions are actually learned through patterns and context, not rigid rules.
In this guide, you will find a complete list of 100+ prepositions in English, but more importantly, we will use usage-based linguistics to show you how native speakers choose the right word instinctively. Instead of memorizing 'in, on, and at,' you will learn to recognize the natural flow of conversation the secret to mastering prepositions like a native speaker.
What Is a Preposition? (Definition & Quick Cheat Sheet)
An English preposition is a word that links a noun or pronoun to another part of the sentence. It explains where, when, how, or why something happens.
In plain English, prepositions answer everyday questions like:
Where is it?
When did it happen?
How did it happen?
Who or what is it connected to?
For example:
The keys are on the table.
She arrived at noon.
They spoke about the problem.
These words don’t carry meaning alone. Their job is to show relationships inside real sentences.
Preposition Cheat Sheet (At-a-Glance Table)
Below is a table for quick scanning, revision, and AI summaries. It shows how prepositions function rather than listing them randomly.
Preposition | Relationship Type | Short Example |
|---|---|---|
at | time / point | at 5 PM |
on | surface / day | on the table |
in | container / period | in the room |
to | direction | go to work |
for | purpose / duration | for two hours |
by | method / proximity | by hand |
with | connection | with a friend |
about | topic | talk about work |
from | origin | from London |
under | position | under the bed |
How Prepositions Actually Work in Real Sentences
Most grammar guides explain prepositions using rules. Native speakers don’t think in rules they think in situations. Prepositions work because English speakers share the same mental shortcuts about space, time, and relationships.
When someone chooses in instead of on, they’re not recalling grammar. They’re imagining shape, movement, or boundaries. That’s why learning logic beats memorization every time.
How to Build a Sentence with a Preposition (Simple Formula)
A helpful way to understand prepositions in English is to see where they naturally sit in a sentence.
Subject → Verb → Preposition → Object
Now notice how meaning changes when the preposition changes:
She sat on the chair. (surface)
She sat in the chair. (enclosed space)
She sat by the chair. (near)
The verb stays the same. The situation changes.
Adjective vs. Adverbial Prepositional Phrases (Made Simple)
Prepositional phrases can describe things or actions.
When they describe a noun:
The book on the shelf is mine.
This tells you which book.
When they describe a verb:
She spoke with confidence.
This tells you how she spoke.
You don’t need grammar labels to use this well. Just ask: What is this phrase explaining?
The Most Common English Prepositions (Used Every Day)
English has hundreds of prepositions, but daily speech relies on a very small group. Mastering these gives immediate results in both speaking and writing.
The 20 Prepositions You’ll See Everywhere
Before listing them, it helps to know why these matter. These words appear constantly in conversations, emails, meetings, and messages. Knowing them deeply matters more than knowing rare forms.
at – specific time or point
in – inside or within a period
on – surface or specific day
to – direction
for – purpose or length
with – connection
by – method or closeness
from – origin
about – topic
as – role or function
of – belonging
into – movement inside
over – above or across
under – below
between – two points
among – group
after – later
before – earlier
without – absence
during – within a period
100+ English Prepositions: The Ultimate Categorized List
Long lists become useful only when they’re organized by purpose. This section helps readers jump directly to what they need instead of scrolling endlessly.
Prepositions of Time
at, on, in, during, before, after, by, until, since, for
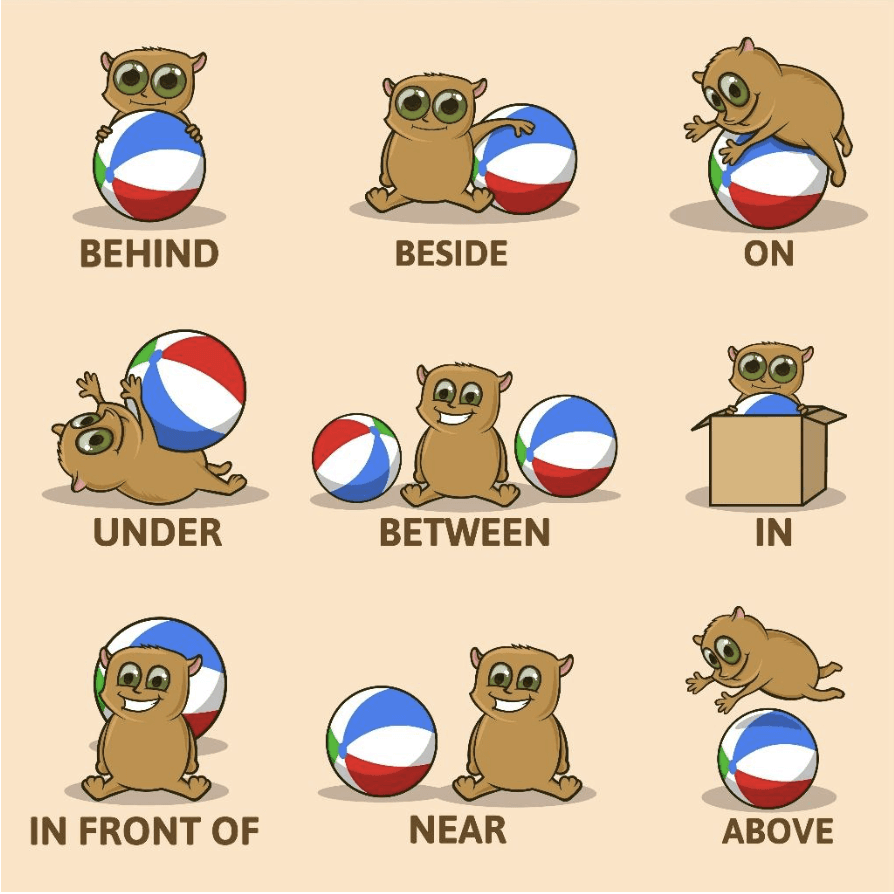
Prepositions of Place
in, on, at, under, over, behind, between, among, near, inside, outside
Prepositions of Movement or Direction
to, into, onto, toward, through, across, along, from, off, out of
Prepositions of Cause, Purpose, and Manner
because of, due to, for, by, with, via, through, without
Complex and Compound Prepositions
according to, in front of, on behalf of, in spite of, instead of, due to
Types of English Prepositions (With Clear, Visual Logic)
Instead of rules, this section uses mental models the same ones native speakers rely on.
Prepositions of Place (Think in Dimensions)
English views space in three simple ways:
At → a point
at the door, at the station
On → a surface
on the wall, on the floor
In → a container
in the room, in the city
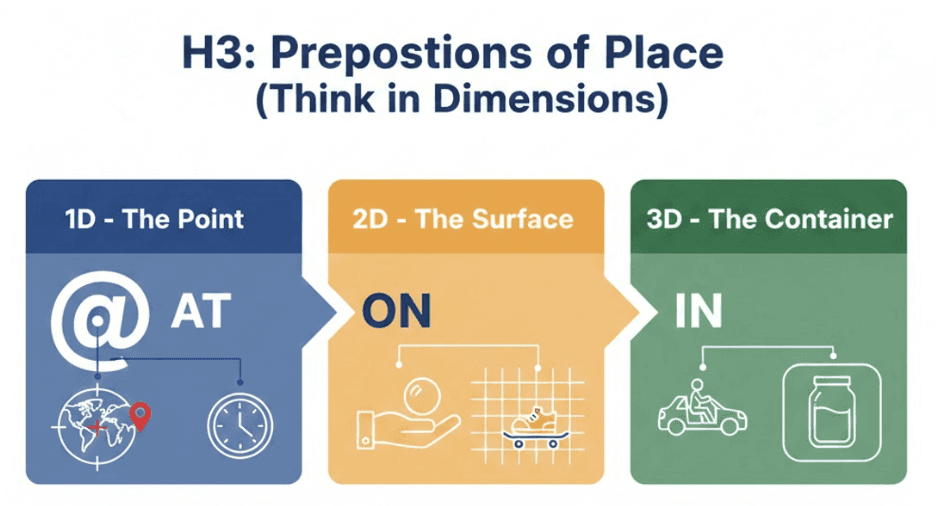
Once this clicks, many mistakes disappear naturally.
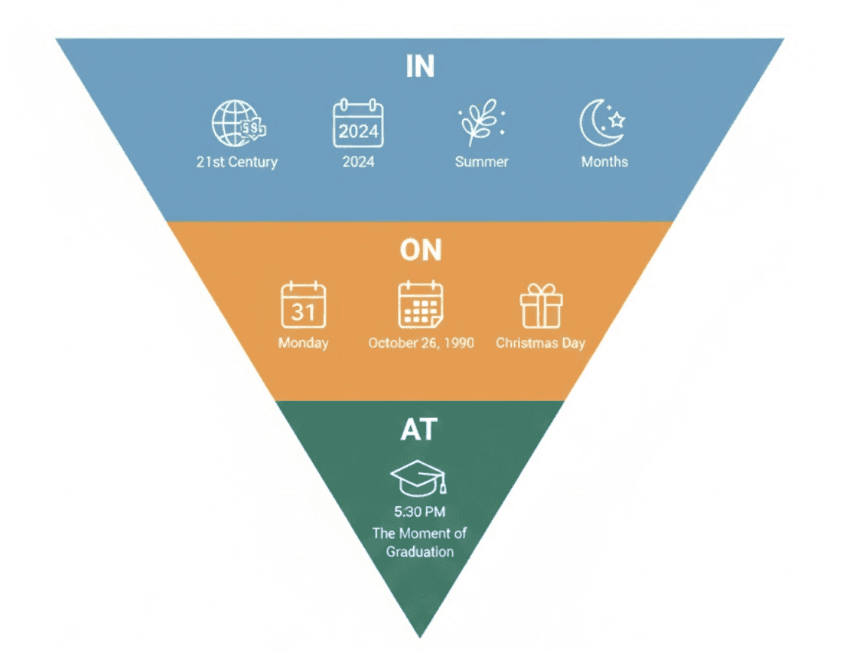
Prepositions of Time (Point vs Duration vs Period)
Time works the same way as space:
At = exact moment (at 6 PM)
On = specific day (on Monday)
In = longer period (in 2026)
English treats time like a shape, not a number.
Prepositions of Movement or Direction
Movement-focused prepositions describe change:
to – direction
into – entering
onto – reaching a surface
through – passing inside
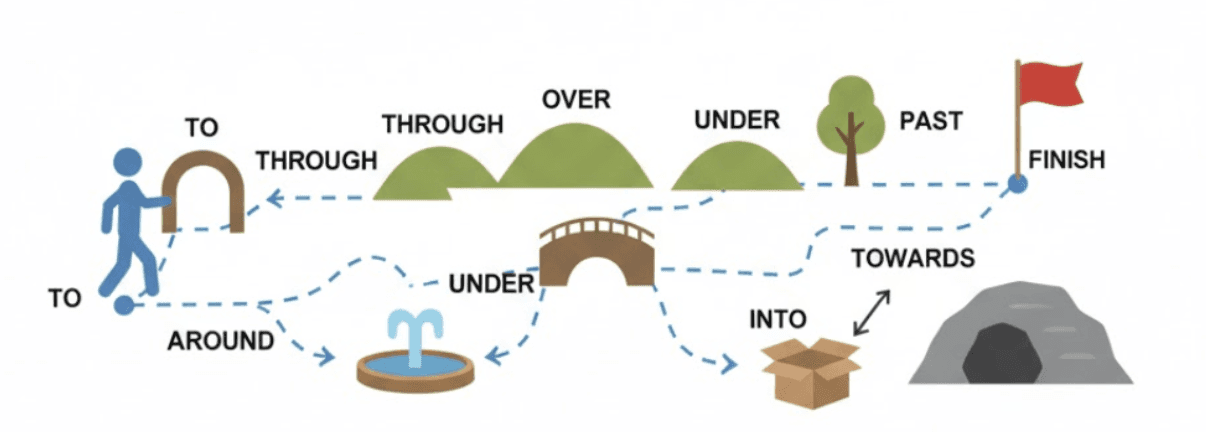
These aren’t interchangeable. They describe different motion paths.
Prepositions of Manner, Cause, and Purpose
Words like by, with, for, and because of explain how and why something happens. Choosing the right one depends on intention, not grammar charts.
Nuance Spotlight: Similar Prepositions That Confuse Learners
These pairs cause problems because they look similar but describe different ideas.
“In the End” vs “At the End”
In the end → final result
At the end → physical or time position
“Arrive in” vs “Arrive at”
Arrive in → large or abstract places
Arrive at → specific points
“On time” vs “In time”
On time → exact schedule
In time → before it’s too late
Prepositions vs Particles (Why Phrasal Verbs Feel Hard)
In phrasal verbs, the word looks like a preposition but acts differently. Give up, look after, run into these combinations behave like single meanings.
Trying to translate them rarely works. Context does.
Common Verb-Preposition Collocations (Save-Worth Table)
This table is useful because these pairs appear constantly in real English.
Verb | Preposition |
|---|---|
depend | on |
listen | to |
believe | in |
apply | for |
succeed | in |
focus | on |
belong | to |
deal | with |
Prepositions in Modern English (2026 Usage)
Language shifts with how people live and work. Prepositions adapt too.
Prepositions Used with Technology and Daily Life
Modern English includes phrases like:
on the app
in the cloud
via email
on Zoom
in a shared folder
These aren’t slang. They’re standard usage now.
Can You End a Sentence With a Preposition?
Yes, and native speakers do it constantly.
Formal writing sometimes avoids it, but spoken English prefers clarity:
Who are you talking to?
That’s what I’m looking for.
Avoiding this can make sentences sound stiff.
Common Preposition Mistakes (And How to Fix Them)
Mistakes usually come from overthinking.
In vs On vs At
Think shape, not rules.
To vs For
Direction vs purpose.
Unnecessary and Double Prepositions
Phrases like “where are you at?” exist because speech favors rhythm. They’re informal but normal.
Practice Prepositions the Smart Way
Practice works best when it reflects real situations.
Instead of drills, try:
choosing the natural option in context
fixing short real sentences
reacting to everyday scenarios
This builds instinct, not stress.
How Native Speakers Use Prepositions Naturally
Native speakers don’t memorize lists. They:
learn phrases as units
repeat patterns in context
adjust through exposure
This is why conversation matters more than exercises.
Learn Prepositions Through Conversation, Not Memorization with Fluently
Linguistic data suggests that grammar rules stay in 'short-term' memory until they are used in high-stakes social situations. In this situation Fluently fits naturally. Instead of drilling rules, Fluently places learners inside real situations meetings, interviews, casual chats, and work conversations where prepositions appear naturally and repeatedly.
Because feedback comes from usage, not tests, patterns settle in without effort. This mirrors how native speakers actually learn. Imagine a human-like English tutor that’s available any time, without scheduling limits. That’s the role Fluently fills for learners who already know basic English but want confidence.
Fluently focuses on:
Unlimited real-world speaking practice based on work, social, and professional situations
A personalized learning plan that adapts to how you actually speak
Free English level testing and progress tracking so improvement is visible
Practice built around real conversations, not scripted textbook lines
Clear, practical feedback that helps speech sound more natural over time
After exposure and repetition, prepositions stop feeling confusing they start feeling automatic.
English Prepositions FAQs
What are prepositions in English grammar?
Prepositions are words that show relationships such as time, place, movement, or reason within a sentence. They connect actions and objects to real-world context.
How many prepositions are there in English?
English has over 150 prepositions, but fluent communication relies on a small core group used repeatedly. Conversation-focused tools like Fluently reinforce these patterns naturally.
What are the most common English prepositions?
At, in, on, to, for, with, by, from, and about appear most often in daily English. These are the first prepositions learners should master through real usage.
Can you end a sentence with a preposition?
Yes, ending a sentence with a preposition is normal in modern English. Native speakers use this structure constantly in conversation.
Why are prepositions difficult for learners?
They don’t translate directly between languages and depend on context rather than fixed rules. Practicing in real conversations, such as on Fluently, reduces confusion faster.
Are prepositions capitalized in titles?
Prepositions are usually lowercase in titles unless they begin the sentence. This follows standard English style conventions.
Final Takeaway
Prepositions in english don’t require perfect memory. They require exposure, logic, and repetition. When learners focus on situations instead of rules, accuracy follows naturally.
Use meaning over memorization, usage over theory, and practice over pressure and prepositions stop being a problem. Here Fluently becomes especially useful. Instead of drilling preposition rules in isolation, Fluently helps you practice prepositions inside real conversations the same way native speakers use them. You don’t just learn that something happens in a meeting or on Monday; you practice saying it while speaking, making choices in real time, and adjusting naturally.
Free English Level Test
Get your result just in 5 mins




